Leonid KeselmanI am a PhD student at the Robotics Institute, part of the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University, where I work on 3D computer vision. My PhD advisor is Martial Hebert. From 2011 to 2017, I worked at Intel, as part of Intel RealSense. I primarily designed computer vision algorithms for efficient hardware ASICs, including the Intel RealSense R200 and D400 RGB-D sensors. Additionally, I worked on software APIs, active illumination systems, human-computer interaction devices, and helped develop demos for trade shows, including CES 2012-2016. I have an MS in Computer Science (AI focus) from Stanford University, where I was a research assistant for Silvio Savarese and a teaching assistant for Fei-Fei Li (CS131 & CS231N). I have a BS in EECS from UC Berkeley, where I worked in Kris Pister's lab. Email / GitHub / Google Scholar / LinkedIn |

|
ResearchI'm interested in computer vision, machine learning, optimization, graphics and robotics. |

|
Flexible Techniques for Differentiable Rendering with 3D GaussiansLeonid Keselman, Martial Hebert arXiv, 2023 arxiv / code / website / We show how shape reconstruction with 3D Gaussians can be expanded to include differentiable optical flow, colored mesh exports and more. |
|
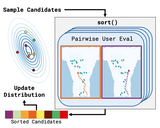
Optimizing Algorithms From Pairwise User PreferencesLeonid Keselman, Katherine Shih, Martial Hebert, Aaron Steinfeld International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2023 arxiv / code / website / We show how to perform efficient black-box optimization of algorithm configuration from user preferences. Results include Intel RealSense stereo cameras and a robot social navigation policy. |
|
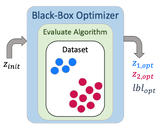
Discovering Multiple Algorithm ConfigurationsLeonid Keselman, Martial Hebert International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2023 arxiv / code / website / youtube / We show the benefits of discovering an ensemble of configurations for a given algorithm during the course of optimization. Results on stereo, planning and visual odometry. |
|
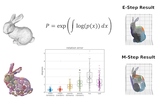
Fuzzy Metaballs: Approximate Differentiable Rendering with Algebraic SurfacesLeonid Keselman, Martial Hebert European Conference on Computer Vision (Oral), 2022 arxiv / code / website / youtube / An approximate differentiable renderer for a compact, interpretable representation, which we call Fuzzy Metaballs. Our approximate renderer focuses on rendering shapes via depth maps and silhouettes. It sacrifices fidelity for utility, producing fast runtimes and high-quality gradient information that can be used to solve vision tasks. |

|
Venue Analytics: A Simple Alternative to Citation-Based MetricsLeonid Keselman ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries, 2019 arxiv / code / slides / website / A bibliometric/scientometric project. Our main two results are a method of assigning value to all venues in computer science and a method to organize them into distinct subfields, all without using citation data. The resulting venue scores can be used to rank universities’ by scholarly output, and produce a responsive author-level metric. |
|
Direct Fitting of Gaussian Mixture ModelsLeonid Keselman, Martial Hebert Computer and Robot Vision Conference, 2019 arxiv / code / slides / website / A formulation for fitting Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) directly to geometric objects, such as a triangular mesh. This method produces more robust results and produces an improvement in 3D registration for both meshes and RGB-D frames. |
|
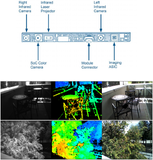
Intel RealSense Stereoscopic Depth CamerasLeonid Keselman, John Iselin Woodfill, Anders Grunnet-Jepsen, Achintya Bhowmik CVPR Workshops (Computational Cameras and Displays), 2017 arxiv / Technical and design details of the Intel RealSense R200 and D400 series |

|
Rigid-body Dynamics for Articulated Mesh TrackingLeonid Keselman, Sterling Orsten, Stan Melax CVPR Workshops (HANDS), 2015 slides / An invited talk for the HANDS 2015 workshop at CVPR 2015. This includes further details about the efficiency of our rigid-body solver, our machine-learning tools, and some details about our data annotation process. |

|
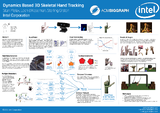
Dynamics Based Hand TrackingStan Melax, Leonid Keselman, Sterling Orsten Graphics Interfaces, 2013 arxiv / code / Using a physics engine (e.g. a dynamics solver) to track 3D articulated objects in real-time. |
|
Dynamics Based Hand TrackingStan Melax, Leonid Keselman, Sterling Orsten ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, 2013 poster / A tracking algorithm that was real-time on a consumer laptop. Won Best Poster Award. |
Intel ProjectsBesides my work on the RealSense depth sensors and the publications above, a sampling of my publicly disclosed work |

|
Intel RealSense 400Intel 2016-08-15 My responsibilities included system performance, components of the stereo algorithm on the imaging ASIC, and contributions to the design of laser projector pattern. |
|
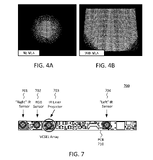
Compact VCSEL ProjectorIntel 2016-06-27 patent / patent #2 / patent #3 / A low-cost dense, configurable projector system for RGB-D depth sensors. |
|
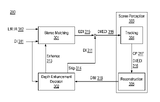
Depth Image EnhancementIntel 2015-08-06 patent / Algorithms to filter, enhance and clean-up RGB-D data streams. |

|
Real-time Box MeasurementIntel 2015-04-08 video / video #2 / Using a single depth sensor, real-time detection of cuboids, accurate estimation of their dimensions, and even some bin-packing. |
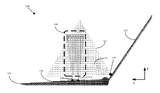
|
DashPoint: A low-cost, low-power human interface deviceIntel 2013-06-07 patent / patent #2 / Finger tracking on a microcontroller, with optics tricks and some HCI ideas |
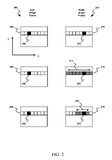
|
Stereoscopic depth reconstruction with probabilistic pixel correspondence searchIntel 2012-07-24 patent / A fast method for performing stereo depth maps. |
Other ProjectsThese include coursework, side projects and unpublished research work. |
|
Dice Stacking: A Dynamic Manipulation TaskCMU 16-741 Mechanics of Manipulation 2018-12-05 paper / video / code / With Hunter Goforth, we designed a manipulation task and solved it with imitation learning. |

|
Introspective Neural NetworksCMU 16-824: Visual Learning and Recognition 2018-05-15 paper / Using pre-trained neural networks to improve fine grained recognition via style transfer. |

|
Stochastic Sampling of Parametric PoliciesCMU 16-745: Dynamic Optimization 2018-05-05 paper / Using a very simple algorithm to solve some very simple environments |
|
Optimizing for Physical SimulationCMU 16-745: Dynamic Optimization 2018-03-22 code / With Chris Atkeson and Alex Spitzer. Using optimizers to match an observed trajectory. |

|
A Maze BotStanford CS225A: Experimental Robotics 2017-06-12 paper / video / video #2 / Making a 6-DoF PUMA arm solve a maze with real-time vision and tracking. |
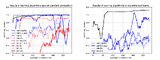
|
Learning Implicit Communication StrategiesStanford CS234: Deep Reinforcement Learning 2017-06-10 Work with Aaron Goodman on used reinforcement learning to discover implicit collusion strategies in the context of an iterated prisoner’s dilemma. |
|
Computational models for text summarizationStanford CS224N: Natural Language Processing 2017-03-18 paper / video / code / poster / Work with Ludwig Schubert on simplified encoders stages for text summarization. |

|
Superresolution MicrscopyStanford CS371: Computational Biology in Four Dimensions 2017-03-16 code / slides / An implementation of Faster STORM using compressed sensing. |

|
Automatically building Restaurant OntologiesStanford CS270: Modeling Biomedical Systems 2017-03-15 paper / poster / Using the Yelp dataset of reviews to model the semantics and relationships between cuisines, businesses and other properties useful for restaurant recommendations. |

|
Beyond Correlation Networks for the Financial MarketStanford CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis 2016-12-07 paper / Using graph models, we track the development of financial networks over the 20th century. |

|
Gradient-learned Models for Stereo MatchingStanford CS231A: Computer Vision, From 3D Reconstruction to Recognition 2016-06-07 paper / code / Some re-implementations of standard stereo correspondence algorithms, along with experiments using classification for stereo matching. |

|
Multimodal Natural Language InferenceStanford CS224U: Natural Language Understanding 2016-06-06 paper / video / We explored how natural language inference tasks can be augmented with visual data. |
|
CNNs for 3D Model ClassificationStanford CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition 2016-03-08 paper / poster / 3D shape classification by learning an embedding function into a 2D image and using a pre-trained ImageNet network. At the time, got state-of-the-art results for single-view classification on ShapeNet40. |
|
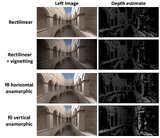
Wide-angle Stereo LensesStanford CS448I: Computational Imaging and Display 2016-03-07 paper / poster / We introduce various projection functions in the analysis of stereoscopic depth sensors. |

|
Doctor BayesStanford CS221: Artificial Intelligence 2015-12-12 website / paper / code / poster / Detecting disease from a short description of symptoms. In some small testing, obtained nearly 90% top 5 accuracy and about 60% top 1 accuracy |
|
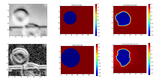
Level-set based tracking and segmentationStanford CS279: Structure and Organization of Biomolecules and Cells 2015-12-04 paper / code / We implemented a detection and deformable tracking pipeline for red blood cells. |
|
Dequantization of Depth DataOther 2015-04-22 code / An O(1) time algorithm for producing smooth normals for quantized data, such as the Kinect. |
|
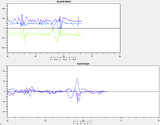
Golf swing monitoringOther 2011-07-21 Work with Ankur Mehta, built a demonstration platform that used wireless low-weight, low-cost sensor platforms to monitor a golf swing. |

|
Project Tetra: Collaborative robot state estimationUC Berkeley EE149: Embedded Systems 2011-07-21 With Humphrey Hu, Ryan Julian, and Eric Yuan, a project to show the efficacy of multiple-robot collaborative state estimation. Using Wiimote cameras, mobile robot platforms, and real-time wireless communication. |

|
GINA: Low power designUC Berkeley 2010-08-22 For testing and validating the functionality of the GINA (Guidance and Inertial NAvigation) mote, a 1.6 gram sensor platform. |

|
GINA: Wireless sensor platformUC Berkeley 2010-06-22 I helped Anita Flynn and Thomas Watteyne build these small sensors and wrote firmware. |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website |